A Pragmatic Utility Function to Describe the Risk-Benefit

It is not straightforward to simultaneously evaluate the beneficial and harmful effects of pain management, since different drugs may possess different analgesia and adverse effect profiles. Utility functions, derived from the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of individual outcome parameters, have been constructed to address this problem. Here, we construct “pragmatic” utility functions based on measurements of benefit and harm, but without making assumptions about the underlying pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Using data from two previous studies, utility functions were designed by estimating the probability of occurrence of benefit and harm and combining these into one function. Study 1 was a clinical trial on the effect of oral pregabalin on pain relief in chronic pancreatitis patients, with endpoint analgesia and dizziness monitored for 21 days. Study 2 was an experimental study on the effect of intravenous fentanyl on antinociception and respiratory depression in healthy volunteers. From study 1, the utility function was negative the first week of treatment, indicative of the greater probability of dizziness than analgesia, but positive thereafter. From study 2, the utility function showed a nadir 30 minutes after dosing, after which the probability function slowly increased toward zero. A pragmatic utility function based on the probability of two binary outcomes, analgesia and adverse effect, was successfully constructed using data from the two previous studies. The results yielded valuable insights into the utility of treatment and may be highly educative for physicians and potentially used in development of potent analgesics without serious side effects.
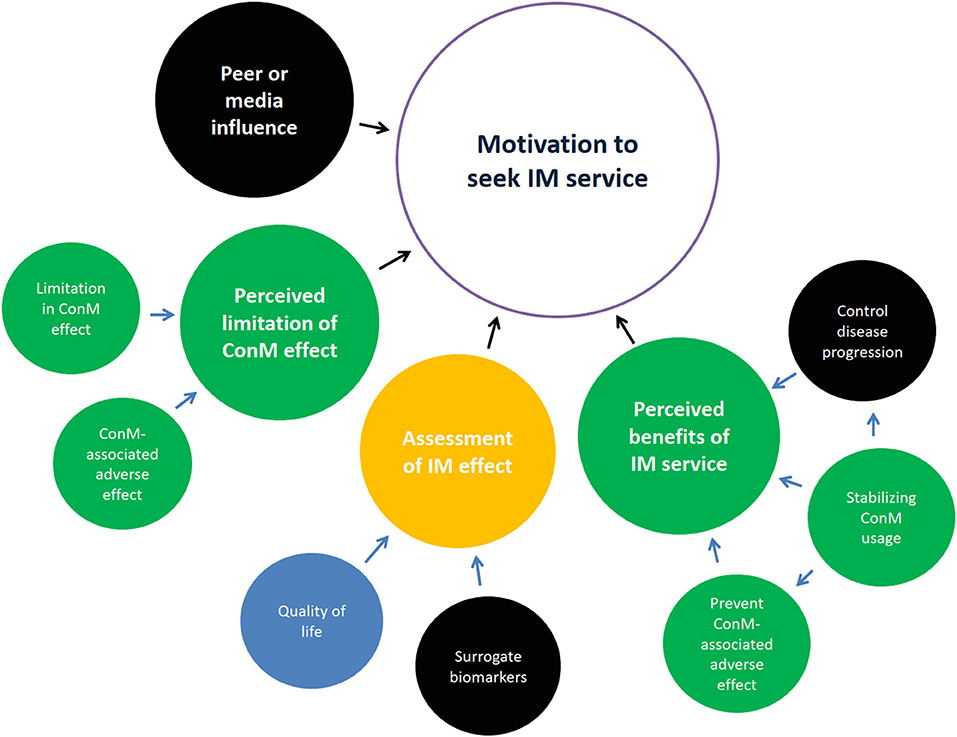
Frontiers PRAgmatic Clinical Trial Design of Integrative MediCinE (PRACTICE): A Focus Group Series and Systematic Review on Trials of Diabetes and Kidney Disease

Role of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) on nociception caused by a murine model of breast carcinoma - ScienceDirect

Addressing the Opioid Crisis: Medical Student Instruction in Opioid Drug Pharmacology, Pain Management, and Substance Use Disorders

A Pragmatic Utility Function to Describe the Risk-Benefit Composite of Opioid and Nonopioid Analgesic Medication

Expected Utility and Risk Preferences
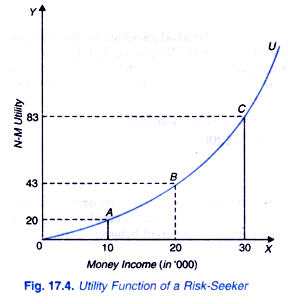
Risk Preference and Gambung: Why Do Some Individuals Gamble?
11.1: App. B: Utility Functions AI Safety, Ethics, and Society Textbook
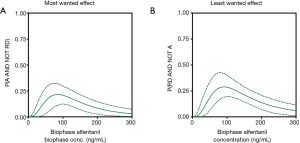
Opioid utility function: methods and implications - van Dam - Annals of Palliative Medicine

Role of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) on nociception caused by a murine model of breast carcinoma - ScienceDirect
Social Sciences, Free Full-Text