Nature and development of plants . The basal portion of the sporo-phyte develops into a massive foot, often provided with rhizoidal-like outgrowths, which serve as a very efficient absorbing organ.The upper portions
Download this stock image: Nature and development of plants . The basal portion of the sporo-phyte develops into a massive foot, often provided with rhizoidal-like outgrowths, which serve as a very efficient absorbing organ.The upper portions of the sporophyte present a remarkableseries of differentiations. The outer part of it consists of chloro-phyll-bearing cells in which, for the first time, genuine stomataappear (Fig. 199, ch). Within this zone of chlorenchyma is adome-shaped layer of spore mother cells alternating with sterilecells which in some genera develop as elaters. In the center ofthe sporophyte is a mass o - 2AXH45J from Alamy's library of millions of high resolution stock photos, illustrations and vectors.
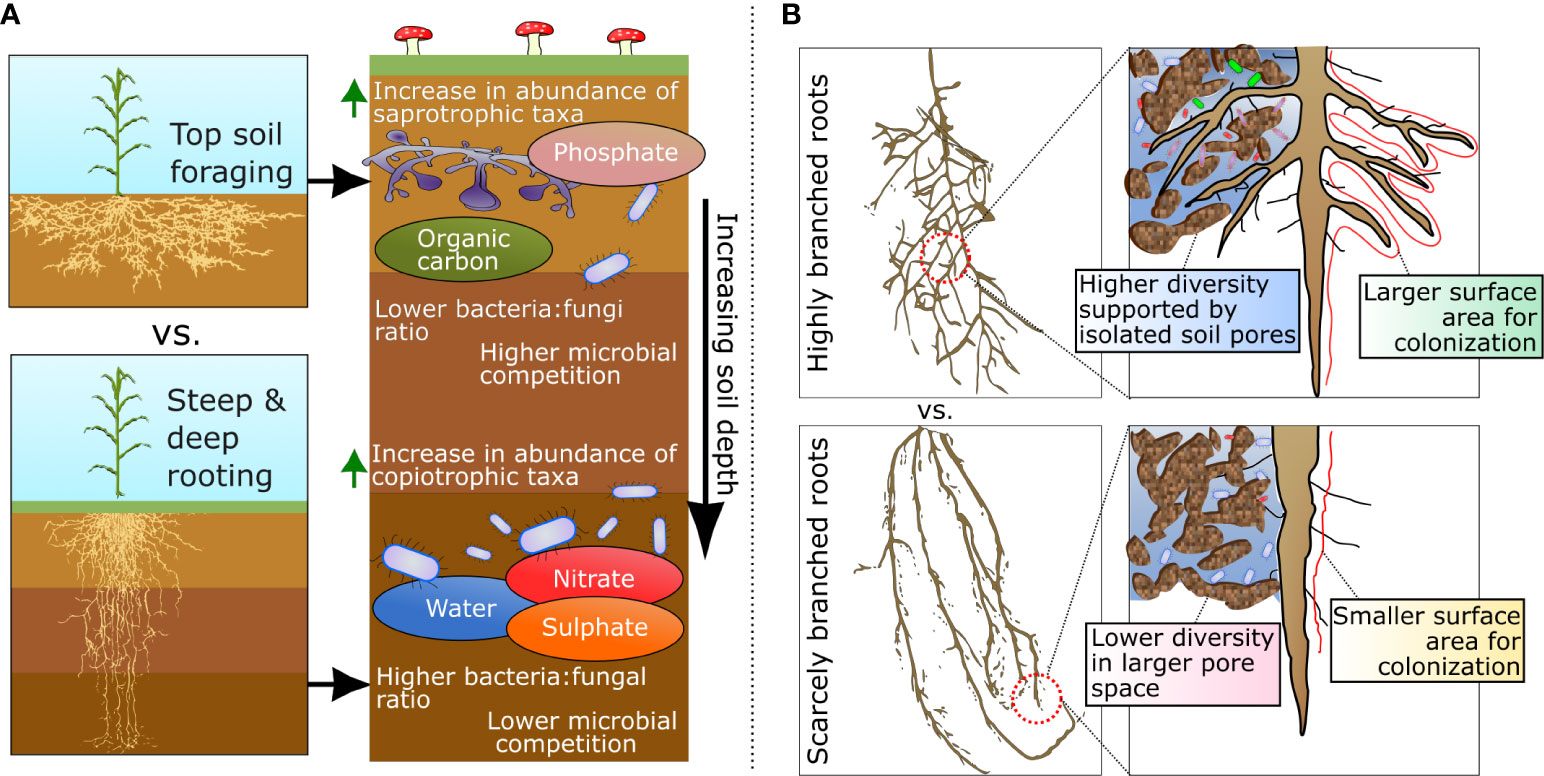
Frontiers Root phenotypes as modulators of microbial microhabitats
Massive organ hi-res stock photography and images - Page 3 - Alamy
Basal layer hi-res stock photography and images - Page 3 - Alamy

Plant - Ferns, Spores, Vascular

The Project Gutenberg eBook of Elementary Botany, by George Francis Atkinson
Systematics and Phylogeny

Foot, plant organ

Nature and development of plants . into an upper part or pileus and a basal region,the stalk or stipe. As this growth proceeds the mass of hyphaeextending from the margin of the

David ingram daphne vince prue peter j gregory science and the garden the scienific basis of horticu by agrihorti - Issuu

Biology botany higher secondary - first year - Textbooks Online