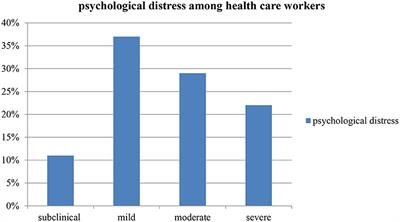
Psychological distress among Iranian health-care providers exposed
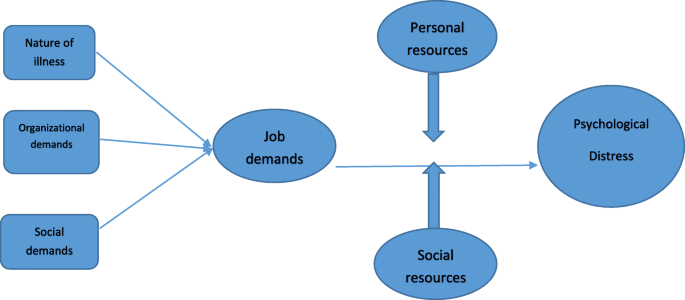
Background Novel corona virus, named COVID-19, has spread rapidly to other countries like Italy, Iran and South Korea and affected all people, especially health-care providers. Therefore, due to the rapid spread of the disease in Iran, the aim of the present study was to explore psychological distress experienced by Iranian health-care providers in the first few weeks of the corona virus outbreak. Methods The present qualitative study was conducted on 18 Iranian health-care providers exposed to COVID − 19 using a content analysis method. Purposeful sampling was used to select the participants and continued until data saturation was reached. Data were collected using semi-structured interviews and then the qualitative data were analyzed through direct content analysis. Results By analyzing 236 primary codes, two main categories were extracted from the experiences of health-care providers during corona virus outbreak. The first category included Occupational demands with three sub-categories: nature of illness, Organizational demands and social demands. The second category was Supportive resources included personal support and social support. Conclusions The results of this study found that there were some barriers and challenges to medical personnel exposed to COVID-19 that caused psychological distress. Some of these problems related to the nature of illness, others related to social and organizational demands and some of supportive resources buffer the relationship between occupational demands and psychological distress.
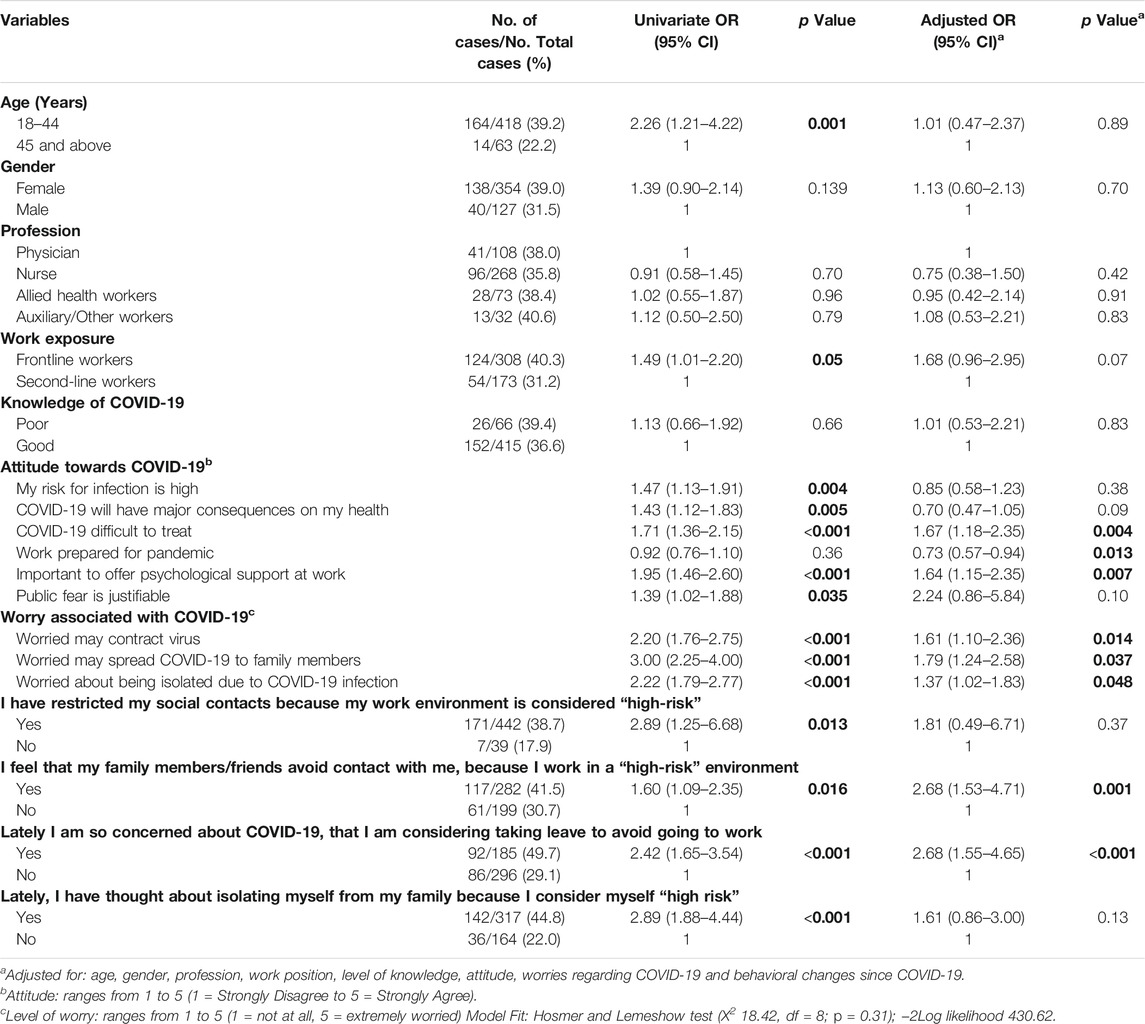
SSPH+ Psychological Distress and Anxiety Levels Among Health Care Workers at the Height of the COVID-19 Pandemic in the United Arab Emirates

Exploring the relationship between mental health literacy and psychological distress in adolescents: A moderated mediation model - ScienceDirect

The Economics of Psychotherapy in Iran

Mental health symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis — JOGH
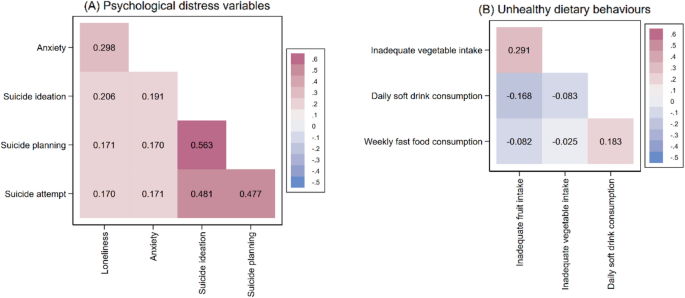
The burden of psychological distress and unhealthy dietary behaviours among 222,401 school-going adolescents from 61 countries

Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and stress and associated reasons among Iranian primary healthcare workers: a mixed method study, BMC Primary Care

Vitiligo and Self-Esteem: Psychological Effects
Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Iran forces women defying hijab laws into psychiatric treatment