Ultrasound imaging - Download as a PDF or view online for free
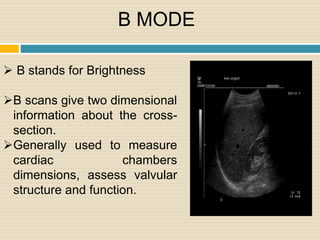
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to visualize internal structures. It works by transmitting sound waves into the body using a transducer probe, which detects the echoes as they bounce off tissues and organs. The echoes are processed to form images on the ultrasound machine screen in real-time. Common applications include obstetrics, cardiology, and urology. The Philips HD11 is an ultrasound system with curvilinear, linear, and phased array probes for different exams. It provides grey scale, Doppler, and color imaging modes. Ultrasound has benefits of being non-invasive, portable, and having no radiation, but has limitations of being operator dependent and unable to penetrate bone.
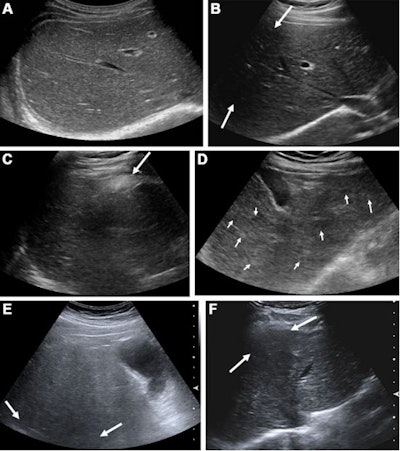
Suboptimal ultrasound imaging leads to higher HCC risk
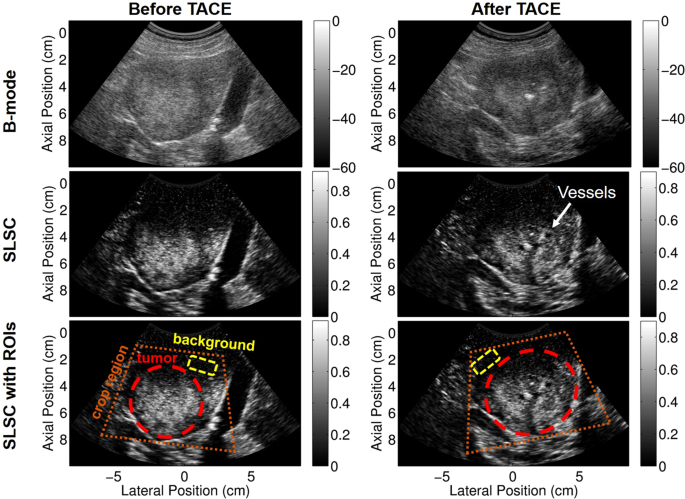
Non-contrast power Doppler ultrasound imaging for early assessment of trans-arterial chemoembolization of liver tumors

The Principles of Ultrasound Imaging

Reading Minds with Ultrasound: A Less-Invasive Technique to Decode the Brain's Intentions
Ultrasound Imaging NYU Langone Health
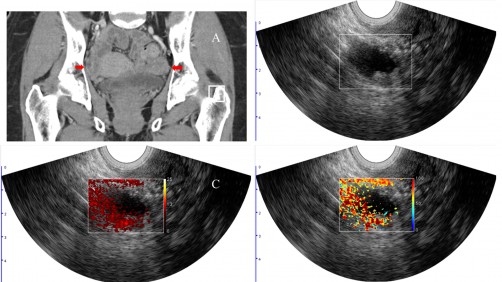
Photoacoustic ultrasound imaging shown to improve diagnostic accuracy of cancerous ovarian lesions - Interventional News
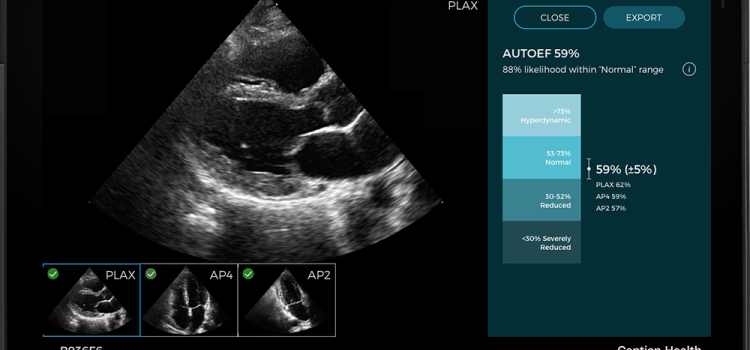
Ultrasound Imaging
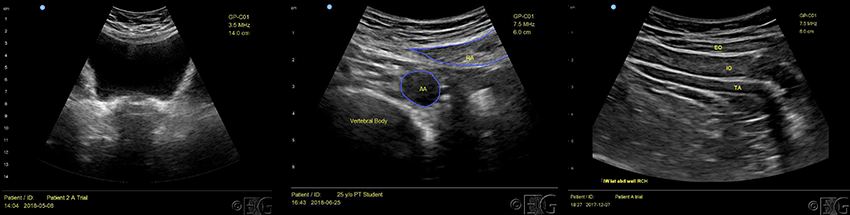
Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging RUSI
Highlight, take notes, and search in the book

Radcases Ultrasound Imaging (Radcases Plus Q&A)


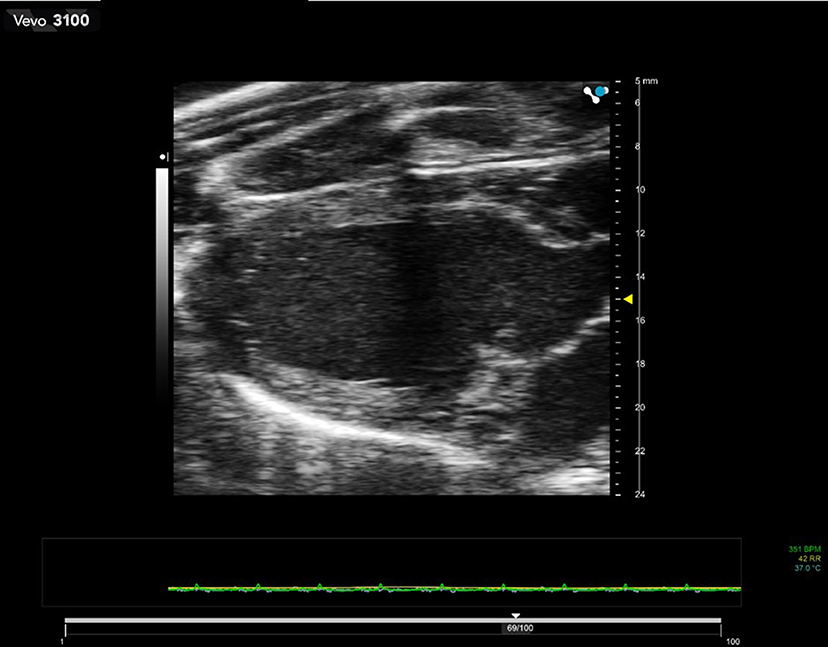



)
