U of T researchers find vulnerability in COVID-19 variants that reduces transmissibility
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that Omicron variants of the COVID-19-causing virus can be hindered in their ability to infect people by mutations in the spike protein that prevent the virus from binding to and entering cells.
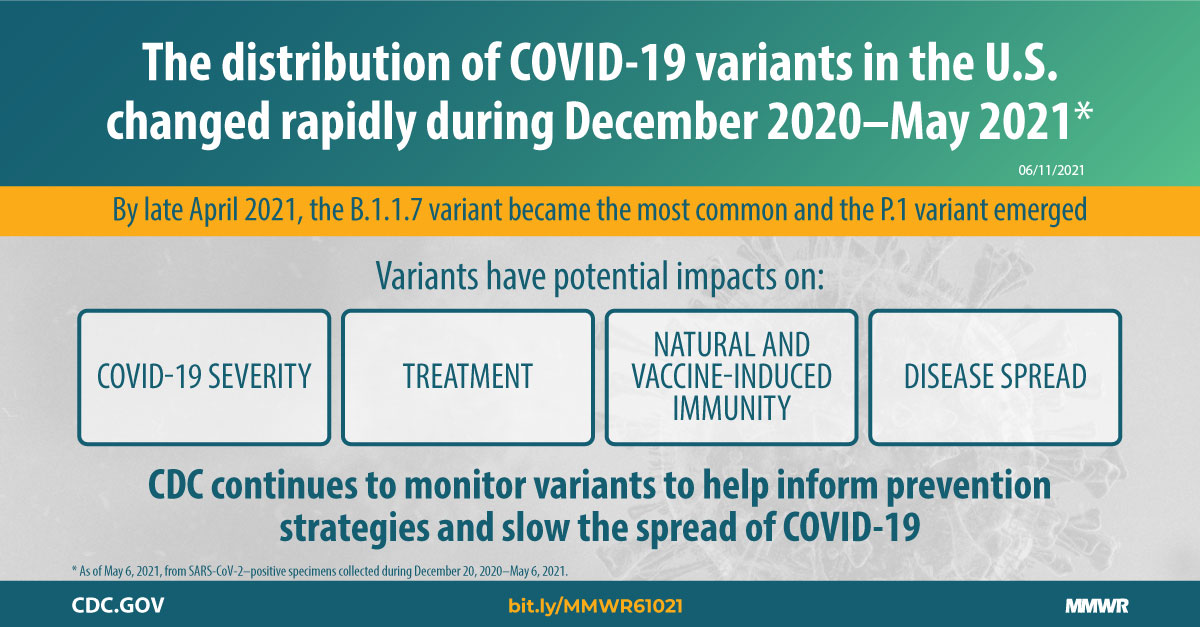
Genomic Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 Variants Circulating in the

What is a variant? An expert explains, News

SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Variant Transmission Within
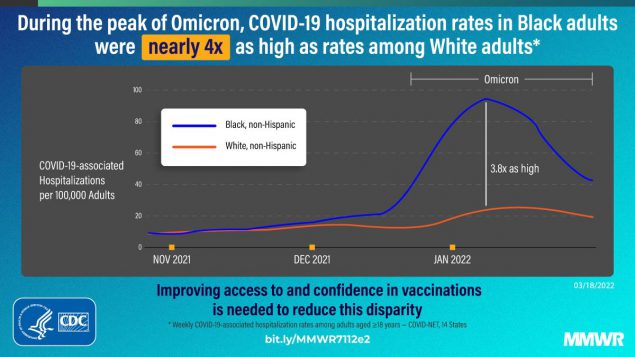
COVID-19–Associated Hospitalizations Among Adults During SARS-CoV
Mutation helps coronavirus infect more cells, study shows - UNC

Medical Research University of Toronto
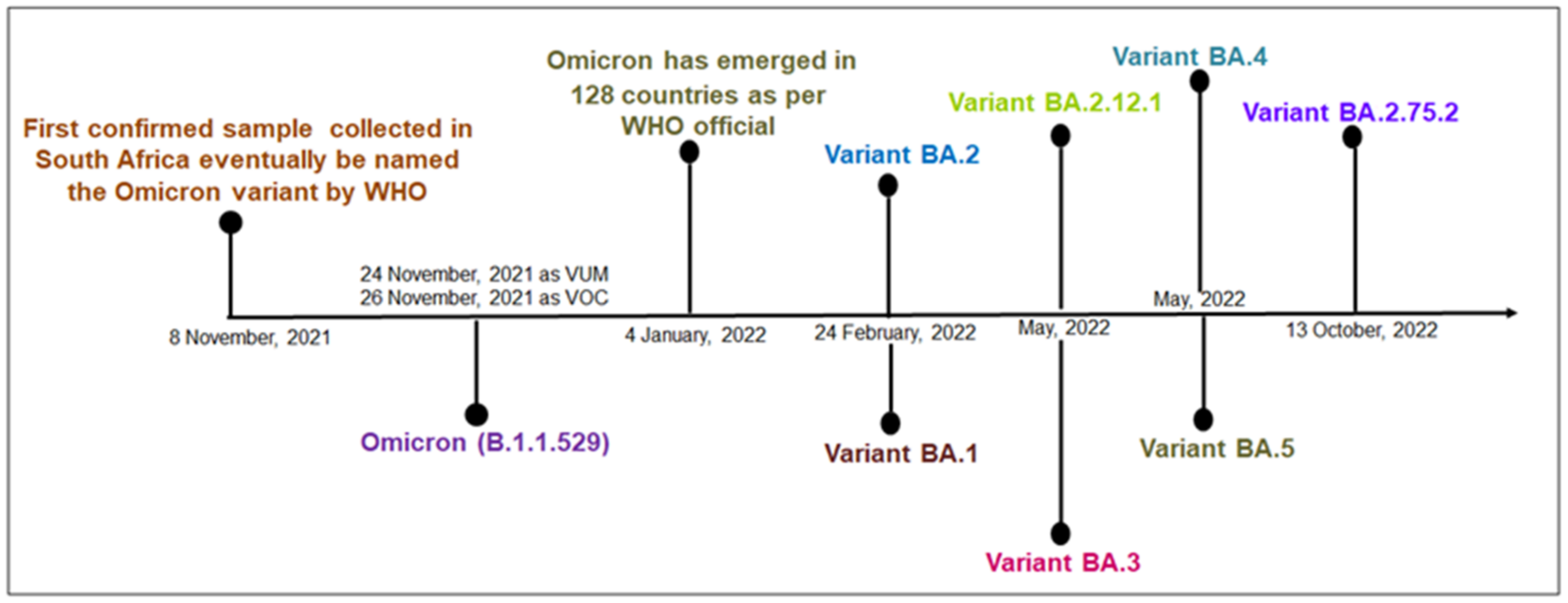
Viruses, Free Full-Text

SARS CoV-2 Delta variant exhibits enhanced infectivity and a minor
Frontier research at the service of the coronavirus epidemic
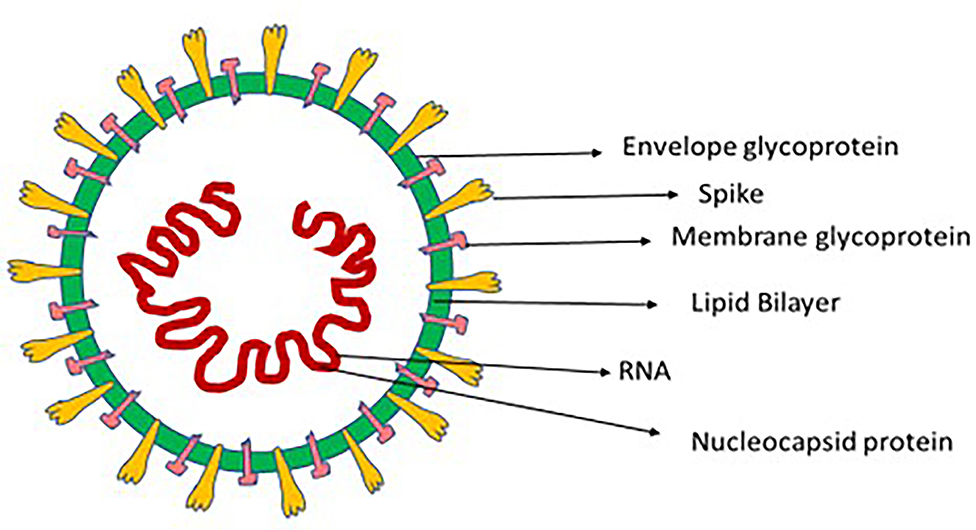
Frontiers Recent Chronology of COVID-19 Pandemic
Medical Research University of Toronto

Map: Where People in the U.S. Are Most Vulnerable to the Delta