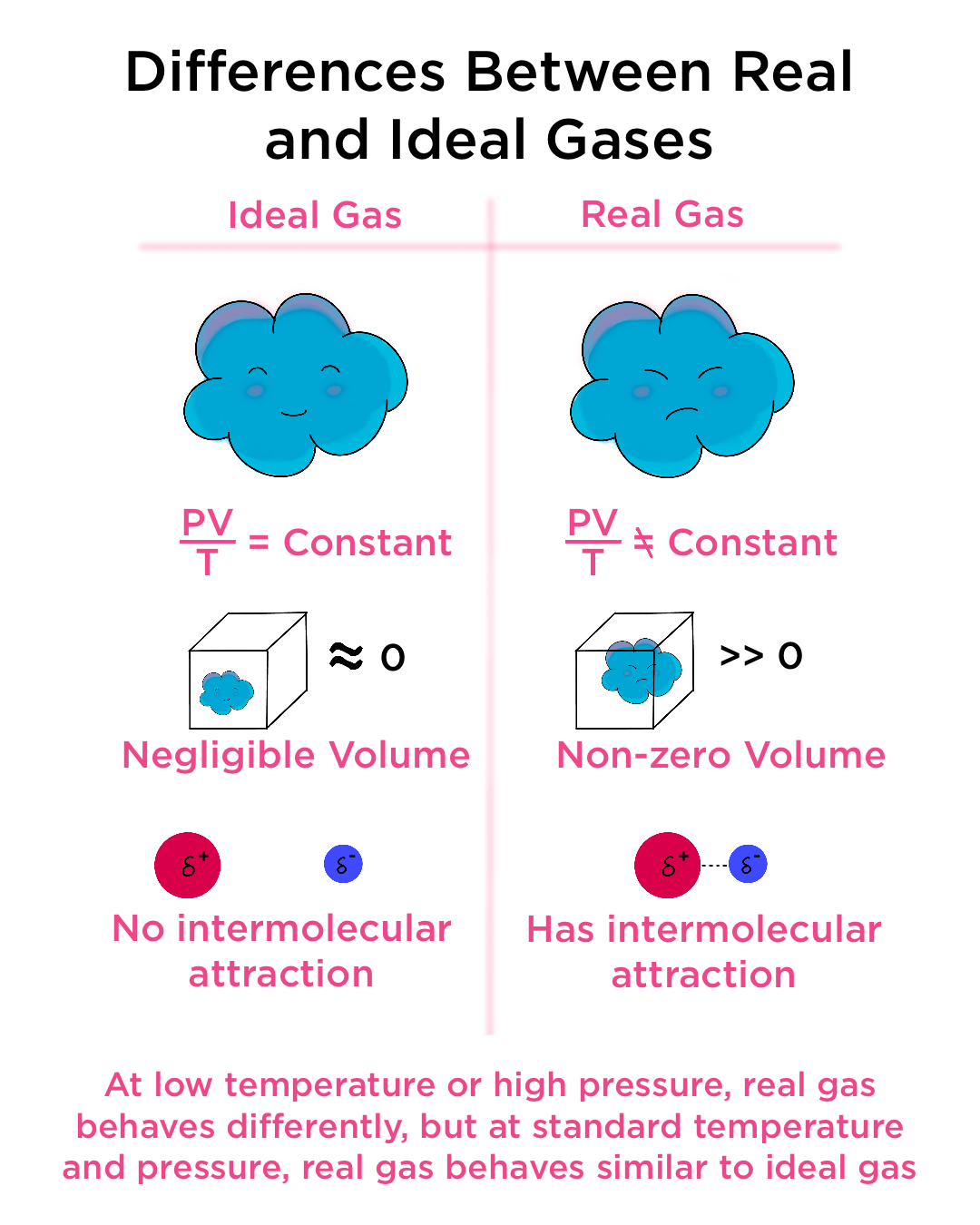
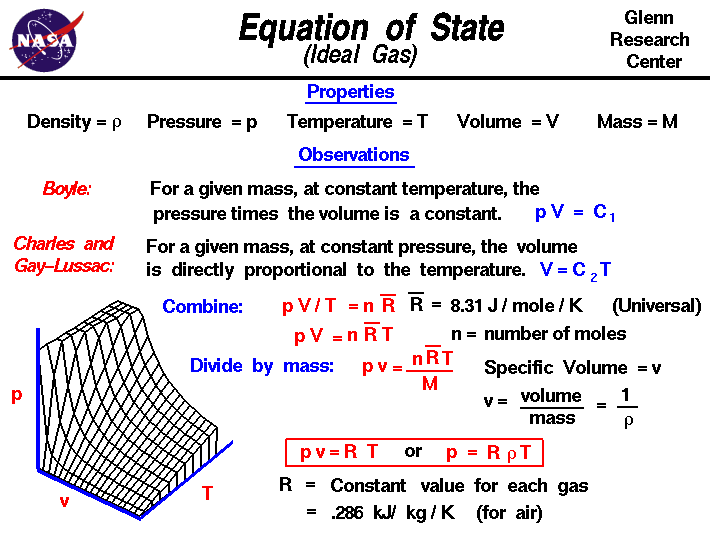
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the …
The empirical relationships among the volume, the temperature, the pressure, and the amount of a gas can be combined into the ideal gas law, PV = nRT. The proportionality constant, R, is called the gas constant. The ideal gas law describes the behavior of an ideal gas, a hypothetical substance whose behavior can be explained quantitatively by the ideal gas law and the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is 0°C and 1 atm.

Chemistry - 2e - Open Textbook Library
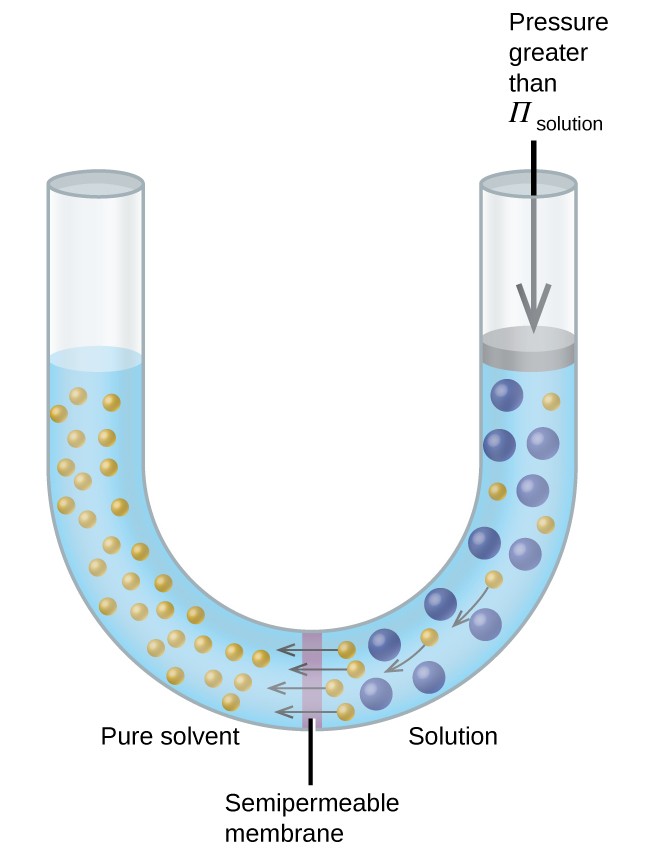
12.5 Colligative Properties – Chemistry Fundamentals
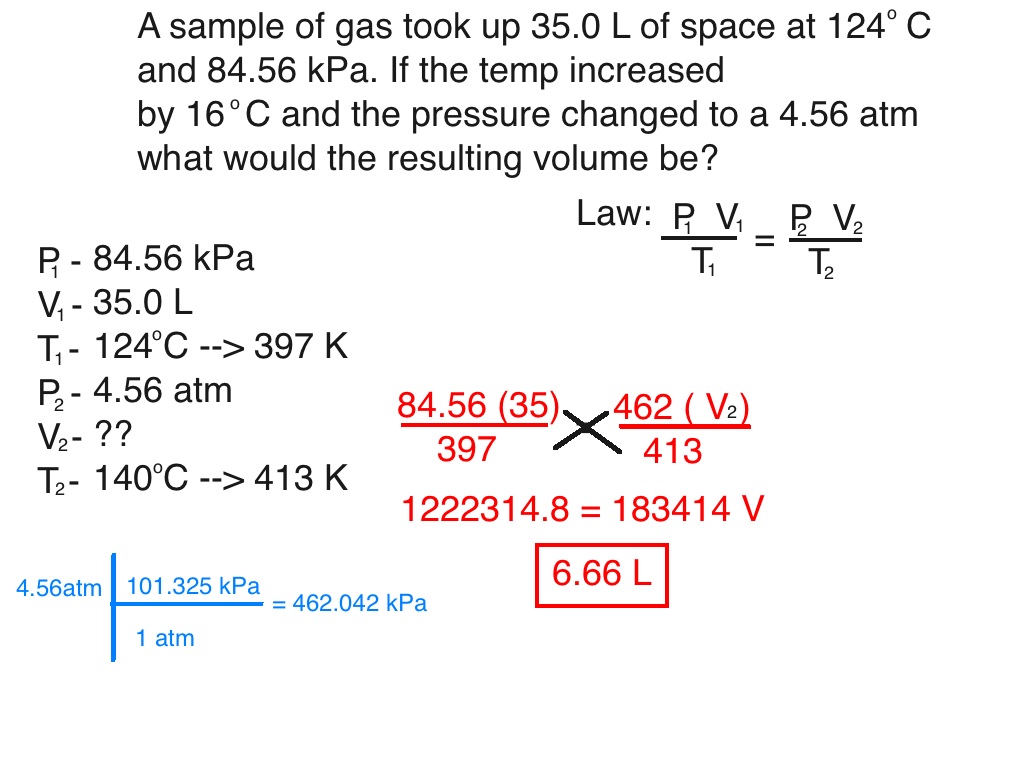
Gas Laws - Chemistry 101

Gas Laws - Equations and Formulas

Atomic Mass Of Pure Aluminum Lab Report
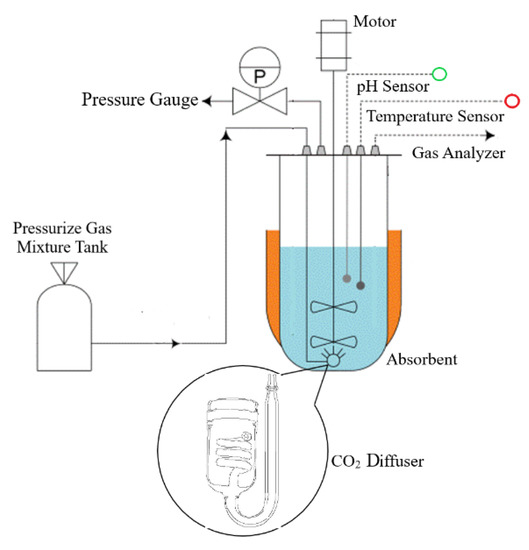
Processes, Free Full-Text
1. An unspecified ideal gas at 10°C and 100kPa occupies a volume of 2.5 m³. (a) How many moles does this gas have? (b) If the pressure and temperature are raised three
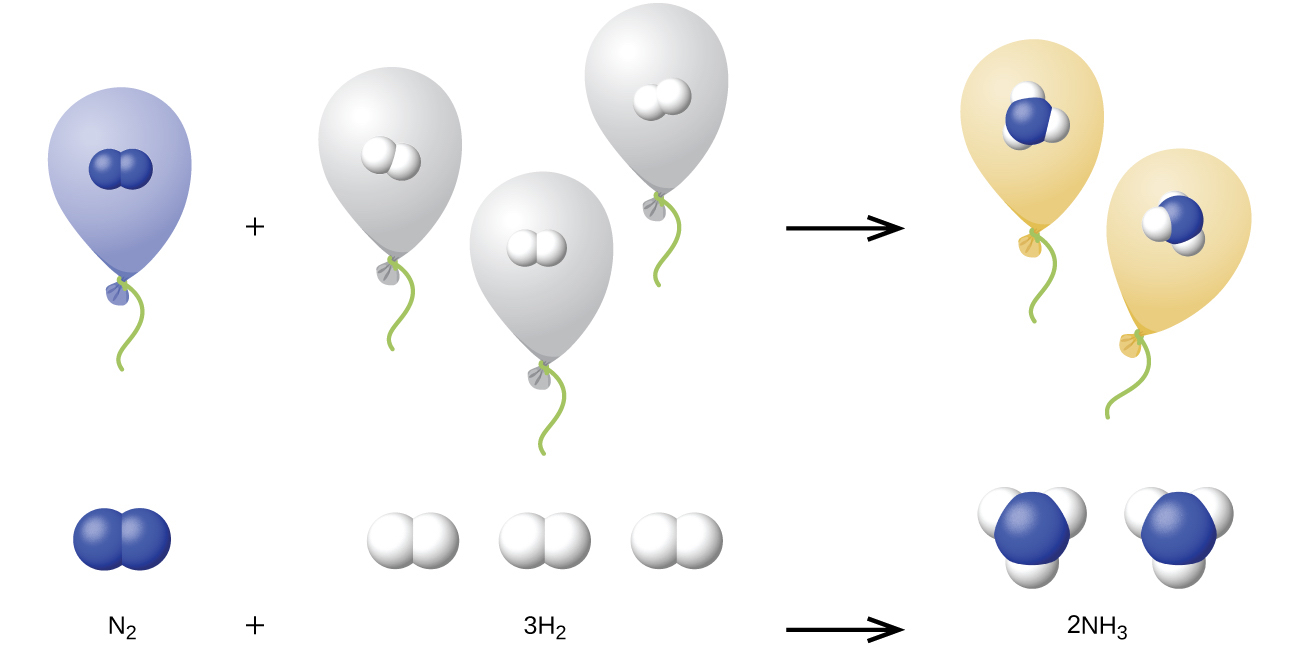
10.4: Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions - Chemistry LibreTexts
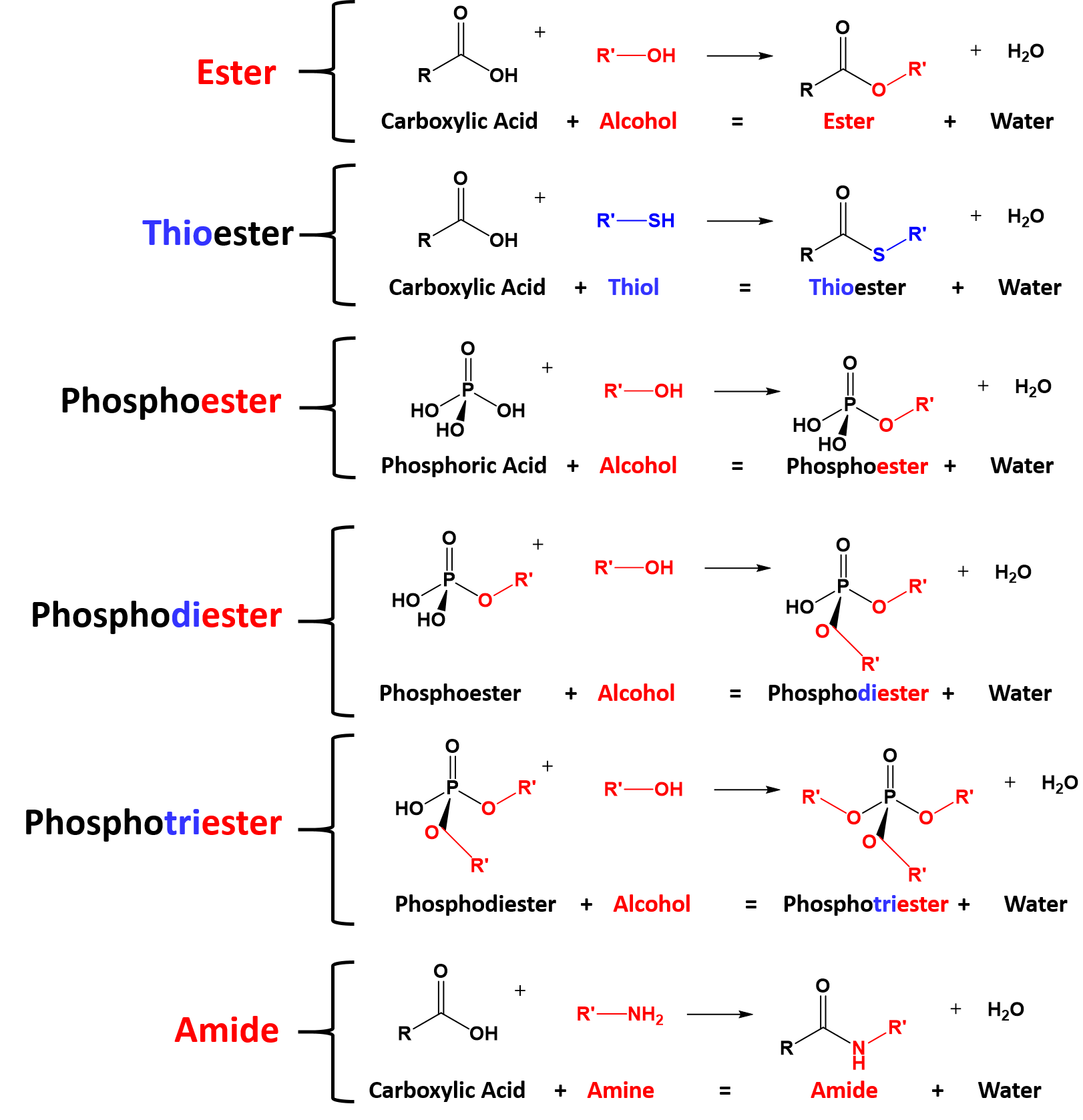
CH105: Chapter 10 - Compounds with Sulfur, Phosphorus, and Nitrogen - Chemistry
Chapter 10 Gas Laws

Chemistry 103-Principles of Chemistry PDF, PDF, Chemical Compounds

Introduction to the Physics of Atoms, Molecules and Photons

Gas « KaiserScience