
Homeostatic regulation of food intake. - Abstract - Europe PMC

The effect of fatty diacid acylation of human PYY3-36 on Y2 receptor potency and half-life in minipigs

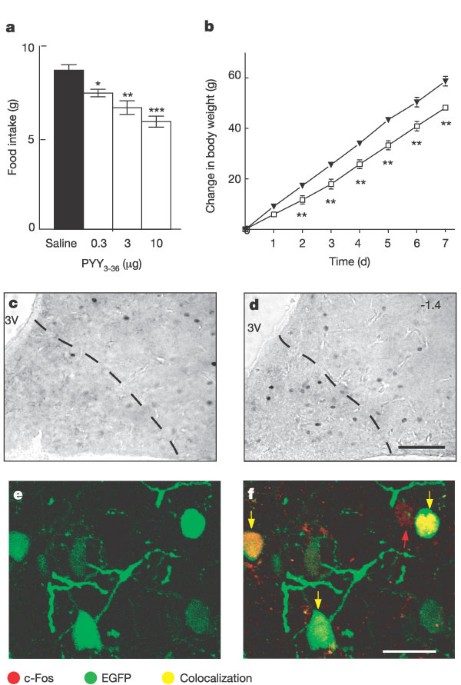
Gut hormone PYY3-36 physiologically inhibits food intake

The Role of Neuropeptide Y and Peptide YY in the Development of Obesity via Gut-brain Axis

Gut-brain signalling - Citizendium

PYY (3-36) protects against high fat feeding induced changes of pancreatic islet and intestinal hormone content and morphometry - ScienceDirect

PYY3–36: Beyond food intake - ScienceDirect

Role of gastrointestinal hormones in feeding behavior and obesity treatment

The Vagus Nerve Mediates the Physiological but not Pharmacological Effects of PYY3-36 on Food Intake

PDF) Physiology: Does gut hormone PYY3–36 decrease food intake in rodents?

Table 1 from Gastrointestinal satiety signals I. An overview of gastrointestinal signals that influence food intake.

Inhibition of Food Intake in Obese Subjects by Peptide YY3–36











/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/ULYR7GA2HRESLEGX3UWK54IDAE.JPG)